By, Mofazzel Hussain, MSc (Chem.), BEd.
The objective of any language classroom is to enable the learners to learn the target language more easily and effectively. The teaching learning process is at its best when the teacher could make involvement of the learners.
To understand the pedagogical aspects of language teaching one has to understand the following terms
a) Approaches. b) Methods. c) Techniques.
It is a way to look at the teaching learning process. It is a theoretical view of what the language is and how it can be learnt.
It describes :
- the nature of the language.
- how knowledge of the language learning is acquired.
- the conditions that promotes the language aquisition.
It referes to the practical implementation of the approach.
It describes :
- the skills to be taught.
- the role of both teacher and student.
- the appropriate procedures and techniques .
- the order in which contents are to be represented.
It referes to the implementation of the procedure that is necessary in teaching a language.
It includes :
- various activities.
- getting students to formulate the answer.
Methods of Language Teaching
- Grammar-Translation Method (GTM)
- Direct Method or Natural Method.
- Audio-Lingual Method (ALM)
- Situational Language Teaching (SLT)
- Community Language Learning (CLT)
- Immersion Method (IM)
- Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
- Bilingual Method
- Content Base Instruction (CBI)
- Competency Based Language Teaching (CBLT)
- Task Based Language Teaching (TBLT)
- Total Physical Response (TPR)
- Whole Languages Approach (WLA)
- Silent Way Approach (SWA)
- Structural Approach (SA)
- Lexical Approach (LA)

Other names of the method are:
- Classical Method
- Traditional Method
Some Noteworthy Points:
- This method was developed by J.V Medinger.
- It has been used to teach the dead language.
GTM emphasize on the following:
- Grammar rules are learnt deductively.
- Translating the sentence to and fro the target language.
Goals of GTM:
- To develop the reading ability of the students, so that they can read literature in the target language.
- To develop students general mental discipline.
Techniques used in GTM:
- Translation of literary passages.
- Drilling of synonyms & antonyms.
- Use of Cognates.
- Deductive application of the rules.
- Fill in the blanks.
- Memorisation.
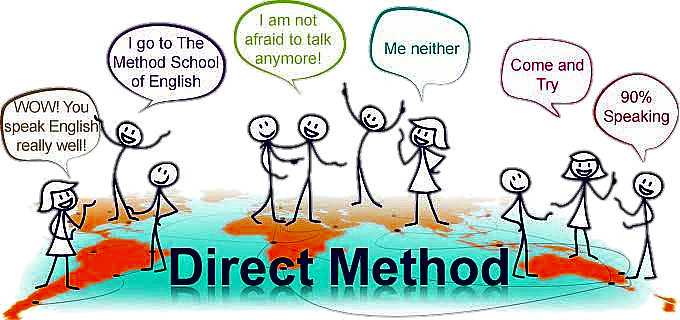
Other names of this method are,
- Natural Method.
- Phonetical Method
- Anti- Grammatical Method
- Reform Method
Some Noteworthy Points:
- It was developed by- Maximilian Berlitz.
- It has replaced- Grammar- Translation Method.
- It also contrasts with- Bilingual Method.
Key Features:
- Language of instruction is Target Language.
- Only everyday vocab & sentences are taught.
- Grammar is taught Inductively.
- New points are taught through Modelling & Practicing.
- Through demonstration, displaying object and pictures, Concrete vocabulary is taught.
- Emphasizes on Correct pronunciation and Grammar .
Techniques used in Direct Method:
- Reading aloud.
- Questions & answers practice.
- Getting students to self-correct.
- Conversation practice. (Teacher – Learners, Learners – Learners)
- Dictation.
- Map Drawing.
- Paragraph Writing.
Advantages of Direct Method:
- Development of four skills of language learning: Listening, Speaking Reading & Writing.
- Convert Passive Vocabulary to Active Vocabulary.
- Full of activities in Direct Method enhances the students’ interests and makes the learning process more exciting.
Another name is Army Method.
Some Noteworthy Points:
- Developed by Charles Fries .
- It contrasts with Community Language Teaching (CLT) method.
- Emphasizes on “Aural/Oral Skills”.
- Based on “Behaviourist Theory”.
Main Features of ALM:
- Grammar is taught Inductively.
- Language Lab is used as a tool.
- Dialogue is the main feature.
- Four skills L-S-R-W are taught and practised separately. But emphasizes mainly on L & S only.
- Give more importance on pronunciation.
- Vocabulary is Strictly limited & learnt in context only.
- Language is taught through Conditioning, stimuli, responses to form new habits of second language
Methods of ALM:
- Dialogue memorization.
- Backward build up drill.
- Chain drill.
- Repeated drilling of structural patterns.
- Single – slot substitution drill.
- Multi-slots substitution drill.
- Grammar game.
- Complete the dialogue.
- Questions answers drill.
- Transformation drilling.

Another name is “Oral Method”
Aim of SLT:
To ensure the practical commands of students on four basic skills LSWR through structures, accuracy in both Pronunciation & Grammar so that students can respond quickly in speech situation.
Goals of SLT:
- Vocabulary Control
- Grammar Control.
Some Noteworthy Points
- Developed by Herold Palmer & A.S Hornby.
- Based on “Behaviourist Theory”
- It bridges the gap between GTM & CLT.
- It replaced the Direct Method.
- It is similar to the Audio-Lingual Method.
Principles of SLT:
- Language learning is habit formation.
- L-S-R-W skills are learnt effectively if they are presented orally first then in the written form.
- Analogy is better than analysis.
Features of SLT:
- Language of instruction is Target language.
- Careful selection of Vocab & Grammar gradation.
- Use of objects, pictures, realia, actions, gestures to demonstrate the meaning of new language items.
Techniques used in SLT:
- Drill based manners of practicing patterns.
- Guided repeatition.
- Question-answers practice.
- Both single-slot & multi-slots drilling.
- Pair practice.
- Group work.

Some Noteworthy Points:
- Developed by “Charles A. Curan”
- Based on “Counseling Approach or “Whole Person Approach“
Features of CLL:
- Teacher as Counselor & Paraphraser.
- Student as Client & Collaborators.
Learning Theory of CLL:
- The CLL view of learning is a “holistic one” as true human learning is both cognitive and affective (termed as whole person).
- Learning takes place in communication situation where both the teachers & students are involved in an interaction.
Aim : To immerge the students in the target language.
Focus on “Repetitive method of learning”
Features of Immersion Method:
- Teacher use realia, visual aids & demonstration.
- Grammar is taught Inductively.
- Regular school curriculum is taught through the target language.
- Emphasize on fluency.
- L-2 (Second Lang.) is vehicle for content instruction.
- Expected to learn other subjects through target language.

Promoted by “Hawatt“
Features of CLT:
- Learning to use English (weak) Vs using English to learn (Strong).
- No bookish rules.
- Emphasizes on Communication from the beginning.
- Learners Centred & Experience based.
- It leads to the conversion of Grammatical Competence to Communicative Competence.
Principle of CLT:
- Communicative Competence is the factor that helps in using grammar appropriately in communication.
- Grammatical Competence implies the ability to use linguistic items correctly and Communicative Competence in addition involves the appropriate use of grammar in communication.

Some noteworthy Points
- Developed by C.J Dodson
- It is the combination of GTM & DM.
Principle of BLM:
- The meaning of words & phrases of foreign language can be taught by using mother tongue.
Features of BLM:
- In this method sentence is the unit of language.
- Mother tongue is used when it is necessary to explain the meaning of difficult words of target language.
- Grammar rules are not taught separately as is done in GTM
Merits of BLM:
- It ensures accuracy in the meaning of words/phrases/sentences to the students.
- It ensures fluency in L-2.
- It is least expensive/ economic.
- It suits majority of Indian Teachers.
- It doesn’t require any trained teacher.

Promoted by, Krahnke.
Goal of CBI:
To prepare students to acquire the L-2 using the context of any subject matter so that students can learn the L-2 by using it within that specific context.
Features of CBI:
- CBI supports contextualised learning rather than isolated L-2 fragments.
- Learners don’t learn through direct instruction, but rather they acquire naturally or automatically.
- Complex information is delivered through real life context, thereby leading intrinsic motivation.
- It provides greater flexibility and adaptability in the curriculum as per students interest.
- It is learner-centred learning.
Promoted by Scheek (1970)
Based on —> Functional & interactional perspective on the nature of language i.e language is learned to be connected to the social context it is used in.
Features of CBLT:
- Preparing students for the different demands of the world.
- L-2 is medium of instruction.
- CBLT has performance-centred orientation.
- Learners are expected to do with L-2.
- Individualized , students-centred instruction.
- Outcomes are made explicit a priori .
Procedure:
- Students are grouped on the basis of their proficiency level, language pace, needs &:goals
- Students have to go through initial assessment.
- CBLT is divided into three steps. In stage 1 & 2;they are dealt with general L-2 competency.
- On the 3rd stage students are grouped on the basis of goal of the learning.
Presented by, Sergio Meza Padilla
Principle:
Language functions as a vehicle for human communication.
Theory:
Language should be learnt as a whole not as fragmented parts.
Features of WLA:
- Four skills are taught together in holistic manner.
- It supports Humanistic & Constructivist Theory.
- Whole Language is said to be Authentic, Personalized, Self-directed, Collaborative & Pluralistic.
- It uses authentic literature rather on artificial.
- It focuses on real & natural events rather than specially designed imaginary events.
- Reading is conducted for the purpose of comprehension.
- Use of students-produced text rather than teacher generated text.
Proposed by Michael Lewis (1993)
Objective:
To make students aware of the use of lexical units, word chunks…etc
Principle:
Language consists of Grammaticalized Lexis not Lexicalised Grammar. In other words Lexis is the central in creating meaning.
Features of LA:
- Giving importance on insight of language lexicon.
- Emphasizes on developing proficiency with lexis.
- Recognises lexis as the basis of language.
- It is alternative approach of Grammar Translation Method.
Procedures of LA:
- Intensive and extensive listening, writting and reading in the L-2.
- L-1 & L-2 comparison & translation.
- Guessing the meaning of vocab items from the context.
- Noticing and Recording language patterns and collocations.
- Working with Dictionary and other reference tools.
Developed by, N.S Prabu
Principle:
L-2 can be learned through the engagement communicative task that compels them to use L-2 for themselves.
Objective:
- To facilitate students language learning by engaging them in a varity tasks.
- To give the opportunity to the students for spontaneous interaction.
Background:
- TBLT has its origin in CLT
- TBLT contrast with GMT
Features of TBLT:
- Students are encouraged to use language creatively & spontaneously through tasks.
- It is learner – centred learning.
- Assessment is based on task outcomes.
Procedure: TBLT follows the following stepwise activities in learning L-2 :
- Pre-task
- Task
- Review
- Report
- Analysis
- Practice
Another name” Aural-Oral Approach
Proposed by, W. Wundt & E.B. Titchener
Principle:
- Structure can be taught by creating adequate situation.
- Oral way teaching is important.
- Language learning is habit formation.
Features of SA:
- Speech practice is important
- Learning L-2 by getting mastery of patterns.
- Provide opportunities to the students to Hear and Speak
- Careful selection & gradation of materials to learn language.
- Words are arranged in suitable order to form suitable patterns.
Developed by, Celeb Ghattengo
It is also named as:
- Humanistic Approach
- Alternative Approach
Features of SWA:
- Teacher keeps silent.
- Emphasizes on students need & students ability.
- Students make their own discoveries, gain their own insights into the functioning of language.
- Students are independent learners
- Translation and rote repetition are avoided.
- Colorful charts are used to learn sounds of the language.
- Evaluation is carried out by observation.
- From the beginning four skills are given importance.
- Role of teacher is as Technician or Engineer.
TLM used are:
- Cuisenaire Rods.
- Sound-Colour Charts.
- Word Chart.
- Fidel Chart.
Goal of SWA:
To get basic fluency in the target language with the aim of being near-native language proficiency.
Principles of SWA:
- Teacher should concentrate on how students learn , not on how to teach.
- Imitation & drilling are discouraged.
- Learning consists of Trial & Error.
- Teacher must not interfere with the learning process.